October 22, 2025
Beyond the Session: Key Takeaways on Revenue Cycle Management Challenges for Critical Access Hospitals
At the 2025 AHIMA Conference, Leah Jeffries, RHIT, CDIP, CCS, CCS-P, Managing Consultant at UASI, presented “The Nuances and Complexity of the Revenue Cycle Management of Critical Access Hospitals,” one of the most critical topics in rural healthcare. This session highlighted how Critical Access Hospitals (CAHs) sustain themselves in a complex regulatory and reimbursement environment and offered strategies for strengthening these lifelines of rural care.
For related insights on performance measurement and organizational support, see our quality and PSI solutions overview.
Setting the Stage: Why CAHs Matter
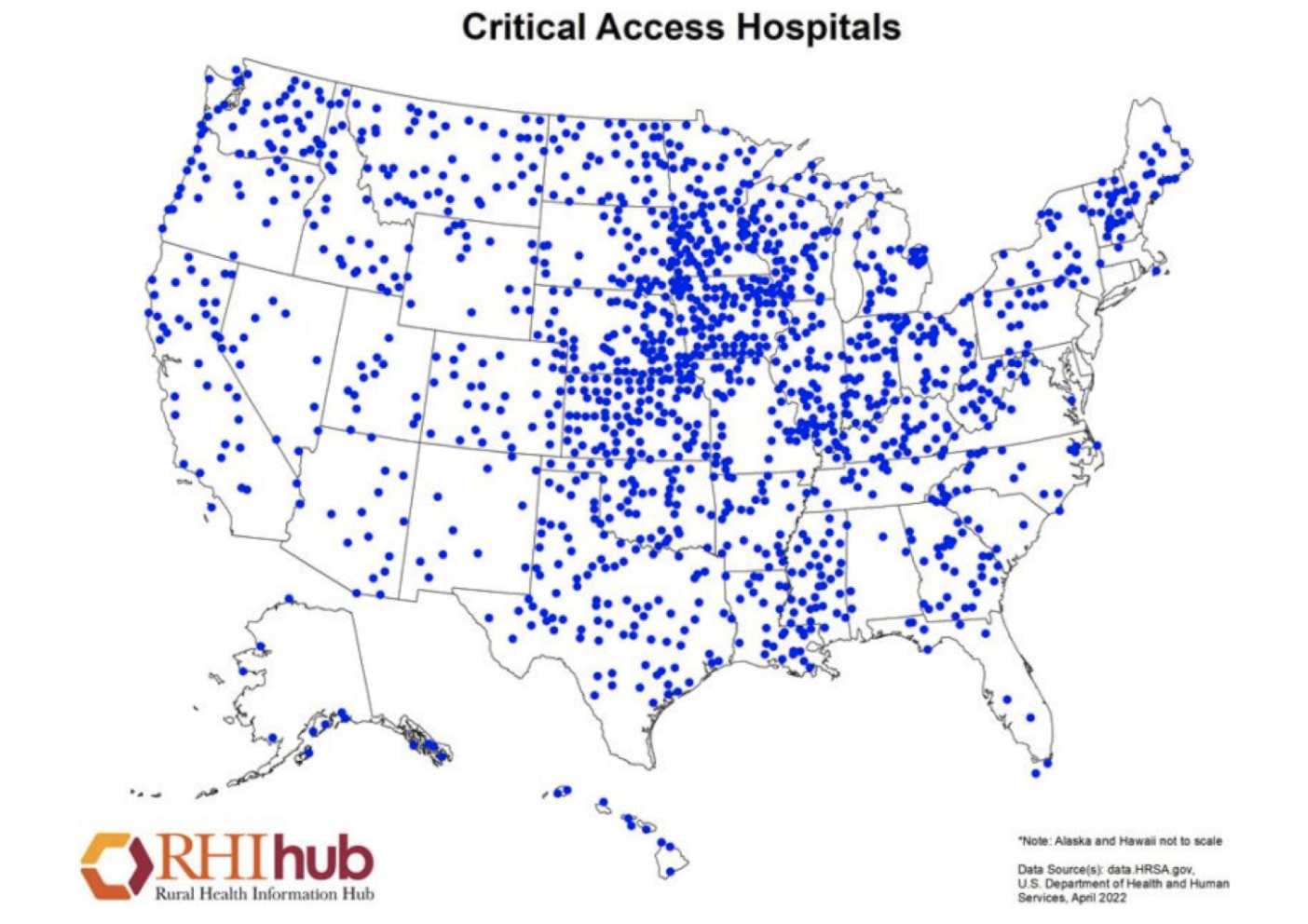
Critical Access Hospitals are essential to improving healthcare access in underserved areas. Established under the Balanced Budget Act of 1997 to counter a wave of rural hospital closures, CAHs today provide inpatient, outpatient, swing-bed, and emergency services to communities that might otherwise face significant travel burdens or care gaps. They remain vital anchors for both healthcare delivery and local economies.
Eligibility and Conditions of Participation
CAHs operate under strict eligibility requirements: a rural location, no more than 25 inpatient beds, an average length of stay under 96 hours, and a defined minimum distance from other hospitals. They must also meet Conditions of Participation (CoP) that differ from acute-care hospitals, including medical staff bylaws, infection control programs, quality improvement initiatives, and state and federal documentation standards. These rules shape daily operations and define compliance expectations.

Revenue Cycle Management in Action
Understanding the nuances of cost-based reimbursement is critical to CAH financial health. Leaders must navigate inpatient, outpatient, and swing-bed payment structures while comparing Method I and Method II billing for professional services to maximize reimbursement. Special billing considerations—such as ambulance services, anesthesia, hospice, and swing-bed care—require careful management to avoid denials and protect revenue streams.
Common coding and billing pitfalls can erode financial stability if left unchecked. Swing-bed billing errors, anesthesia modifiers, ambulance mileage reporting, and charge validation issues are frequent pain points. Strengthening coder training, improving charge capture processes, and building tight feedback loops between coders, billers, and clinical staff can significantly improve accuracy and reduce denials.
Documentation and Compliance: Persistent Challenges
Clinical documentation is often the weakest link in CAHs due to limited staff, rotating providers, and hybrid paper/EHR systems. Common shortcomings include incomplete operative notes, delayed queries, outdated EHR smart phrases, and gaps in medical necessity documentation. Building stronger CDI programs, investing in provider education, and refining EHR tools can close these gaps and support compliant coding.
Surgical and anesthesia documentation also demand special attention. Missing signatures, absent start and stop times, and insufficient specificity can put reimbursement and compliance at risk. Structured templates, routine audits, and physician champions help reinforce best practices and ensure accountability.
Strategies for Success
Successful CAHs leverage data, communication, and training to drive improvement. Cross-training staff, collaborating with other rural facilities, and building community partnerships all strengthen resilience. Regular compliance briefings, simple visual dashboards for leadership, and alignment of financial strategies with clinical priorities are key to sustaining performance.
Preparing for Change: Regulatory Shifts and Rural Resilience
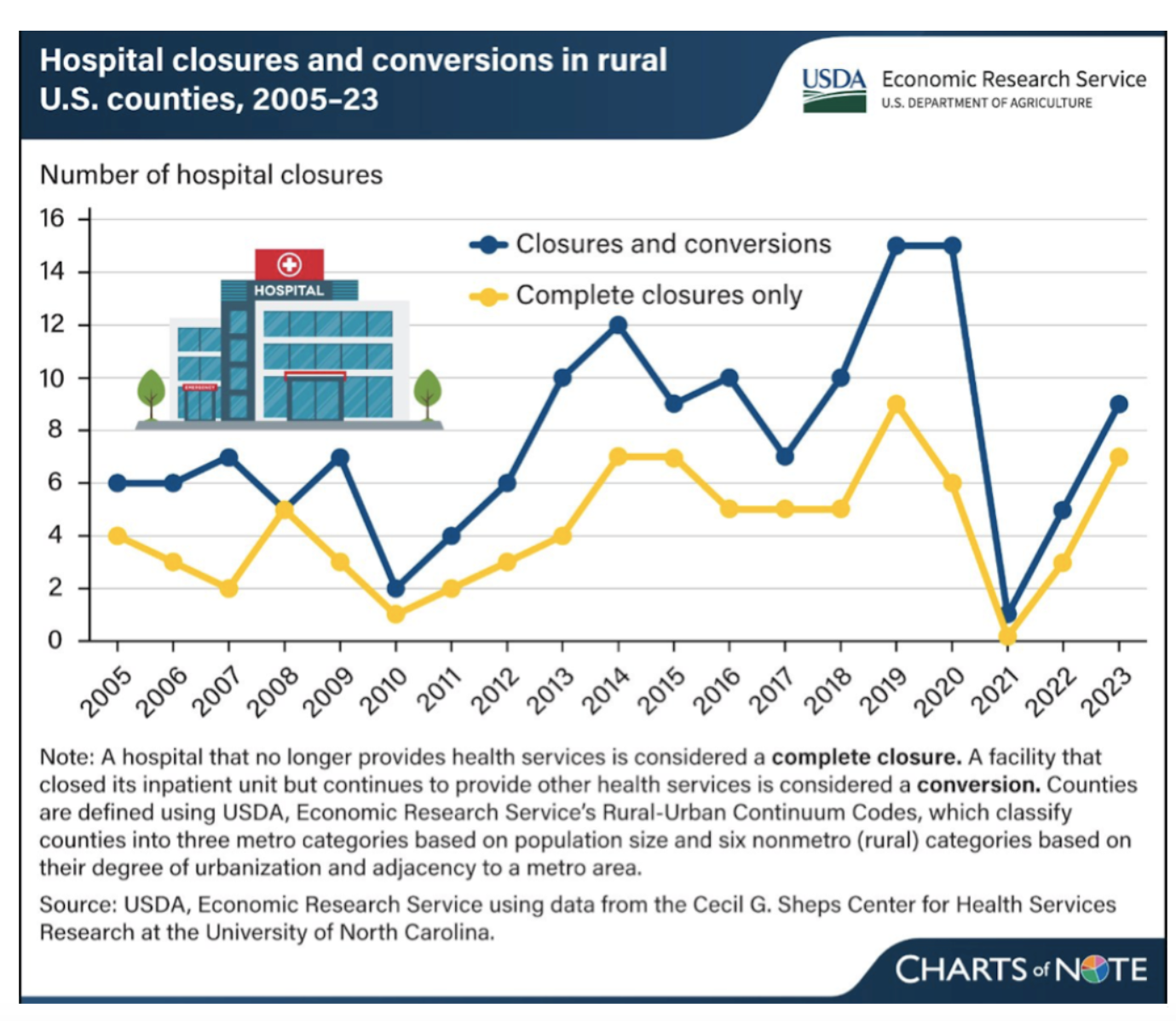
Regulatory and reimbursement changes are constant. Staying ahead requires proactive monitoring of CMS rules, ongoing staff education, and flexible technology solutions. With more than 140 rural hospitals having closed or stopped inpatient services since 2005, the stakes for CAHs have never been higher. Hospitals that anticipate and adapt to these changes can safeguard their reimbursement and maintain access to care for their communities.
Why It Matters
Critical Access Hospitals are more than healthcare providers—they are the backbone of rural communities, creating jobs, stabilizing local economies, and ensuring access to essential services. By adopting stronger revenue cycle practices, improving documentation, and staying current with regulations, healthcare leaders can maintain financial stability, regulatory compliance, and high-quality care close to home.
Final Thoughts
“The Nuances and Complexity of the Revenue Cycle Management of Critical Access Hospitals” highlights a roadmap for action. It offers tools and strategies for leaders to improve coding accuracy, strengthen documentation, and safeguard reimbursement even in resource-constrained environments.
Need Support?
UASI partners with hospitals and health systems to improve revenue cycle management, coding accuracy, and compliance. If your organization is looking to strengthen its processes or navigate the complexities of Critical Access Hospital requirements, our experts can help. Reach out to UASI today to learn how we can support your team.

Leah Jeffries, RHIT, CDIP, CCS, CCS-P
Managing Consultant, Strategy
Leah is a middle–revenue-cycle leader focused on improving coding operations, documentation quality, and financial performance through process redesign and technology-driven solutions. She excels at identifying root-cause issues, breaking down outdated workflows, and leading teams with transparency, collaboration, and hands-on problem solving. A featured speaker at the AHIMA 2025 Conference, Leah brings practical insight into modern middle–revenue-cycle challenges and solutions.
Her MBA equips her with a strong foundation in strategic thinking and organizational leadership, enabling her to align operational improvements with broader business objectives.
Works Cited
National Center for Biotechnology Information. (n.d.). Figure 22: Distribution of critical access hospitals in the United States, 2022. In 2022 National Healthcare Quality and Disparities Report. NCBI Bookshelf.
Available at
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK601637/figure/ch1.fig22/
U.S. Department of Agriculture, Economic Research Service. (n.d.). 146 rural hospitals closed or stopped providing inpatient services from 2005 to 2023 in the United States. ERS Charts of Note.
Available at
https://www.ers.usda.gov/data-products/chart-gallery/gallery/chart-detail/?chartId=103649
Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. (n.d.). Critical Access Hospitals.
Available at
https://www.cms.gov/medicare/provider-enrollment-and-certification/certificationandsurveys/cah
Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. (n.d.). Medicare Claims Processing Manual, Chapter 2: Critical Access Hospitals.
Available at
https://www.cms.gov/regulations-and-guidance/guidance/manuals/internet-only-manuals-ioms-items/cms018912
Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. (n.d.). Critical Access Hospitals Center.
Available at
https://www.cms.gov/center/cah-center