June 3, 2025
Ischemic vs. Hemorrhagic Stroke: Coding and Documentation Essentials
Hemorrhagic Stroke Overview
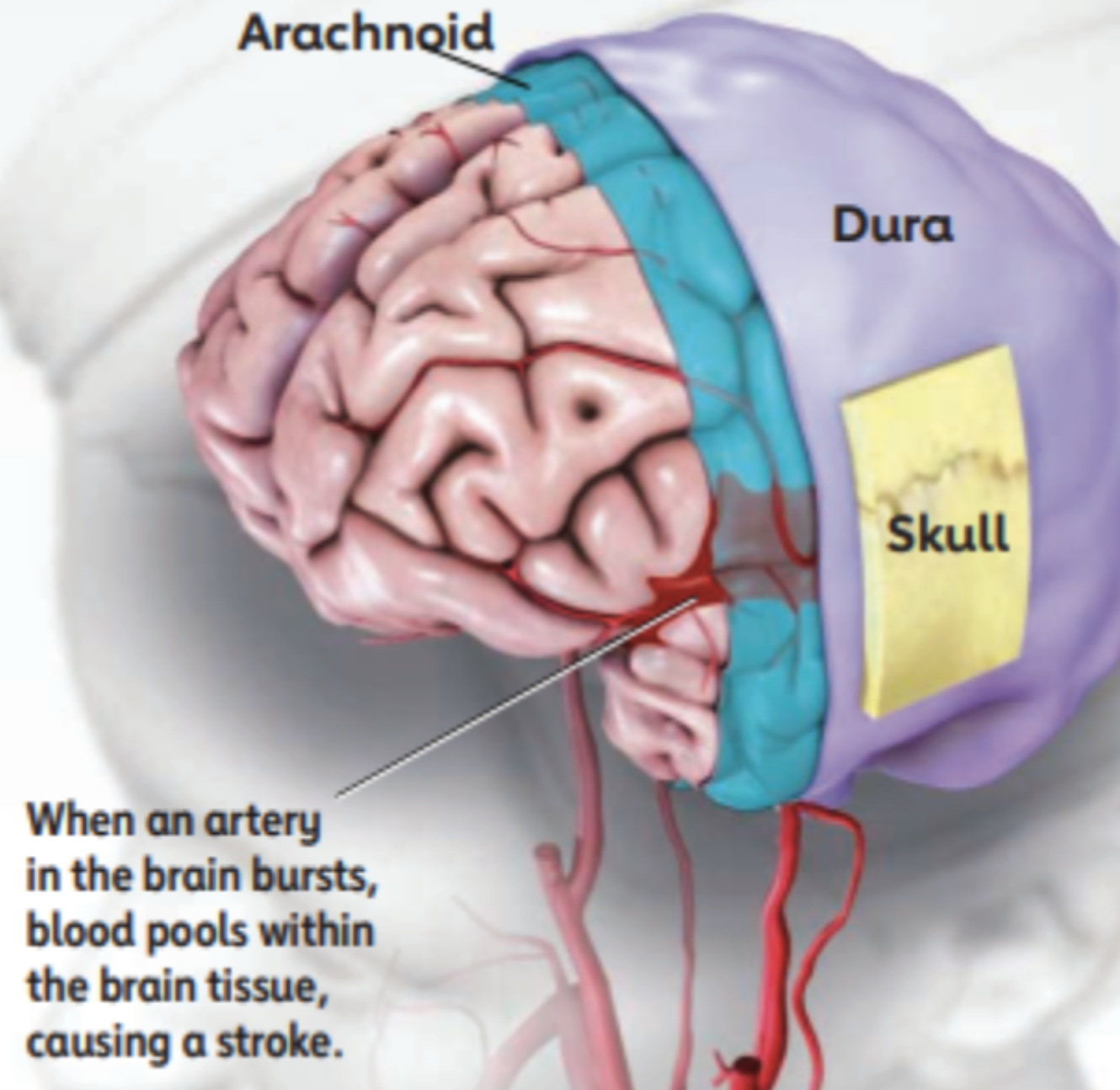
Hemorrhagic Stroke: About 13 percent of strokes happen when a blood vessel ruptures in or near the brain. This is called a hemorrhagic stroke. When a hemorrhagic stroke happens, blood collects in the brain tissue. This is toxic for the brain tissue, causing the cells in that area to weaken and die.
Types of Hemorrhagic Stroke
There are two kinds of hemorrhagic stroke. In both, a blood vessel ruptures, disrupting blood flow to part of the brain. Intracerebral hemorrhages (most common type of hemorrhagic stroke): they occur when a blood vessel bleeds or ruptures into the tissue deep within the brain. They are most often caused by chronically high blood pressure or aging blood vessels. Subarachnoid hemorrhages: Occur when an aneurysm (a blood-filled pouch that balloons out from an artery) on or near the surface of the brain ruptures and bleeds into the space between the brain and the skull.
Ischemic Stroke Overview
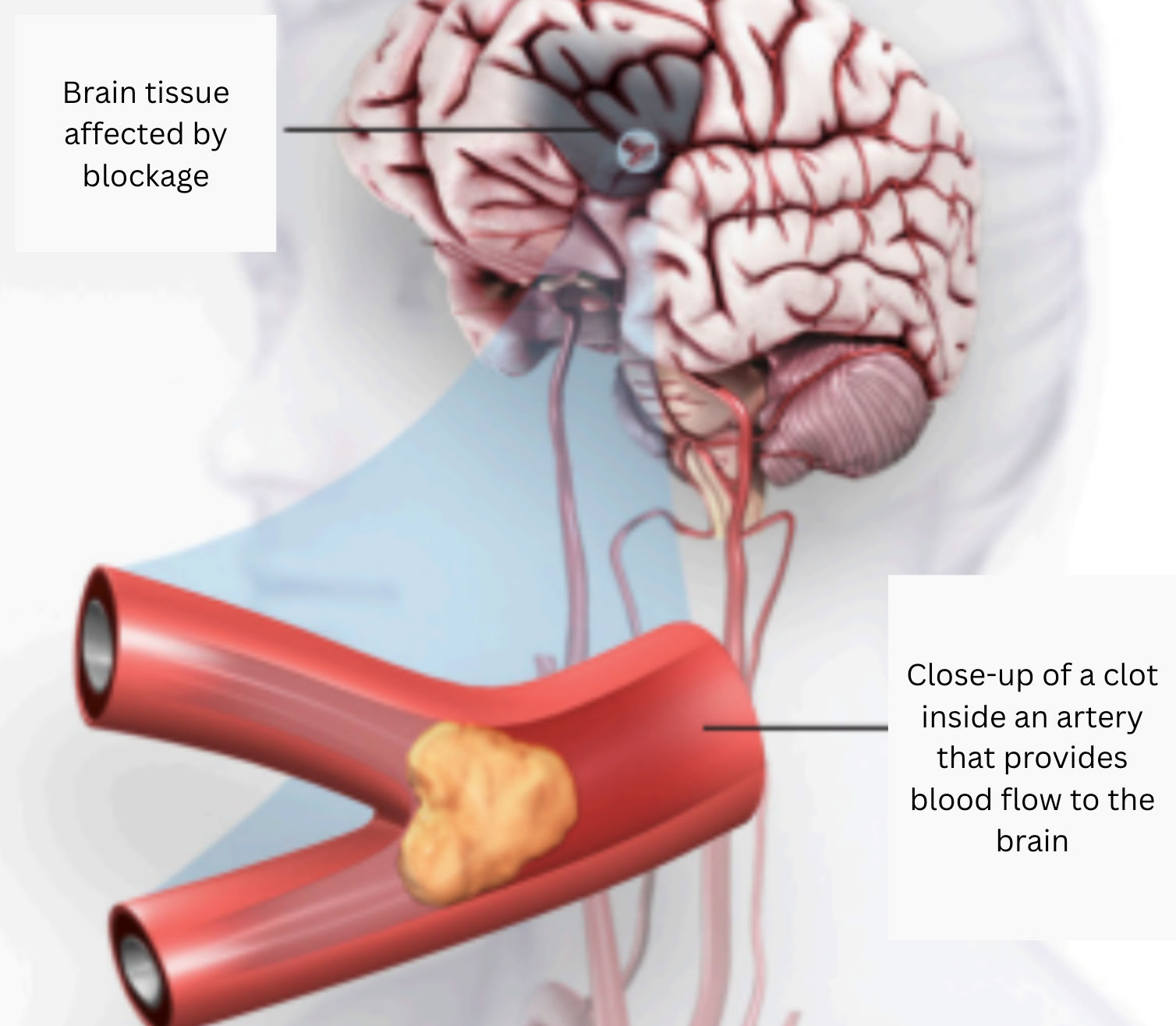
Ischemic Stroke: The majority of strokes (87%) occur when blood vessels to the brain become narrowed or clogged with fatty deposits called plaque. This cuts off blood flow to brain cells. A stroke caused by lack of blood reaching part of the brain is called an ischemic stroke. High blood pressure is a leading risk factor for ischemic stroke
An ischemic stroke occurs when a clot or a mass blocks a blood vessel, cutting off blood flow to a part of the brain.
Types of Ischemic Stroke
There two main types of ischemic stroke. Cerebral thrombosis is caused by a blood clot (thrombus) in an artery going to the brain. The clot blocks blood flow to part of the brain. Blood clots usually form in arteries damaged by plaque. Cerebral embolism is caused by a wandering clot (embolus) that’s formed elsewhere (usually in the heart or neck arteries). Clots are carried in the bloodstream and block a blood vessel in or leading to the brain. A main cause of embolism is an irregular heartbeat called atrial fibrillation.
Stroke Severity, Neurological Deficits, and NIHSS Documentation
Also code: Report all neurological deficits that occur during the hospitalization, even if they resolve before discharge.
Please pay special attention to laterality. When reading the chart, please try to find specificity regarding whether the deficit affects the dominant or non-dominant side of the body.
Also code: NIHSS Scores : The NIHSS is a neurological exam that is scored on all acute stoke patients. The score describes the severity of the stroke from no stroke (score of zero) to severe stroke (score of 21-24). - info from Coding clinic 4th Q 2016 p.61

Jessica Lutz, MBA, RHIA, CCS
AHIMA Microcredential: Auditing: Inpatient Coding
Senior Consultant, Audit at UASI
Jessica Lutz serves as a Senior Consultant in Auditing at UASI and is recognized for her ICD-10-CM/PCS expertise and inpatient coding background. She shares coding tips from an auditor’s perspective, highlighting common pitfalls and practical ways coders and CDI teams can improve accuracy and documentation quality.
Works Cited
American Stroke Association.
(n.d.). Types of stroke.
Available athttps://www.stroke.org/en/about-stroke/types-of-stroke
American Hospital Association. (2016). NIH Stroke Scale reporting. Coding Clinic for ICD-10-CM, Fourth Quarter, 61.